Your Genesys Blog Subscription has been confirmed!
Please add genesys@email.genesys.com to your safe sender list to ensure you receive the weekly blog notifications.
Subscribe to our free newsletter and get blog updates in your inbox
Don't Show This Again.

Until very recently, only 13% of contact centre agents worked remotely on a permanent basis. Now, in an environment shaped by the coronavirus pandemic, that number is rapidly growing.
In its latest report, “The Inner Circle Guide to Contact Center Remote Working Solutions,” ContactBabel surveyed US contact centres about the challenges they’re facing during the COVID-19 pandemic. Among those challenges was the issue of changing workforce conditions — specifically, the need to use remote working solutions to avoid a disruption in customer support operations. Let’s take a look at how US contact centres are responding to the unique demands of the current climate.
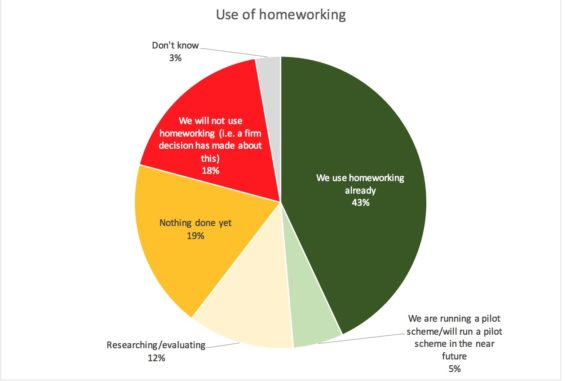
Before the coronavirus outbreak, fewer than half of US contact centres allowed agents to work from home. Of the contact centres surveyed in 2019, 43% allowed at least some of their agents to work from home, while 57% either had made the firm decision to not offer remote work options at all, were in the process of evaluating remote work, or hadn’t made any moves one way or the other.
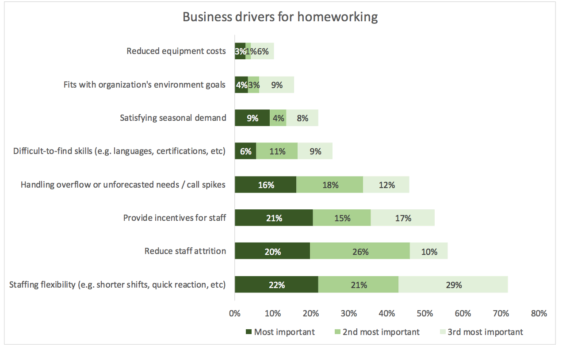
Virtualising multiple contact centres allows agents to move easily from one virtual location to another — and that allows for increased staffing flexibility. And because homeworking gives call centres a large pool of agents to draw from, as needed, it can be a major advantage in handling call spikes.
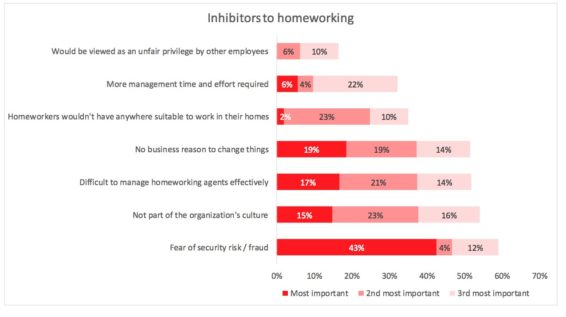
Respondents noted that the fear was home workers would be in unsupervised environments, increasing the risks for data security breaches and fraud compared to workers located in a supervised call centre. This was especially concerning if physical paperwork was involved or the agents had to write down payment details or passwords.
In mid-April 2020, ContactBabel analysts ran a short survey for 108 US contact centres to gauge some of the changes taking place in the industry due to the coronavirus pandemic. While the sample size is smaller than usual, the survey results still offer a flavor of what’s been happening in the industry.
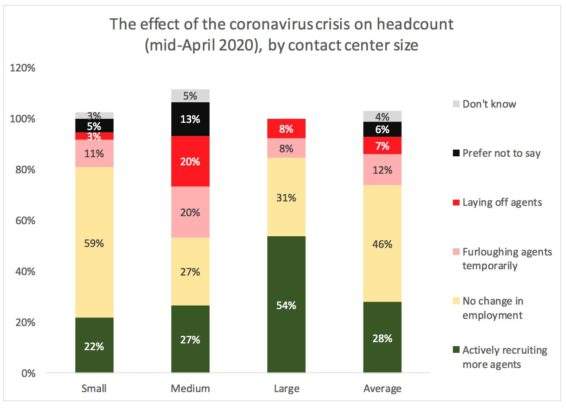
While 7% of respondents had made staff redundant and 12% put some staff on temporary furlough, 28% of contact centres were actively recruiting new staff during the crisis. When segmented by contact centre size, results show that more large contact centres (54%) are actively taking on new staff, while mid-sized contact centres appeared to be the most vulnerable to job losses.
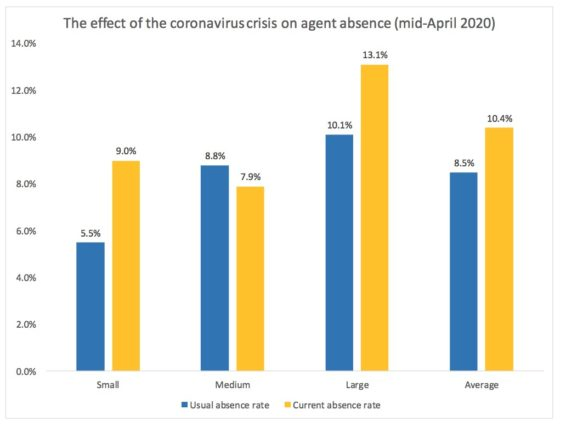
Only 1 in 10 contact centres surveyed were seeing absence rates of over 25%, suggesting that absence due to illness or lack of childcare doesn’t seem to be a problem for most of those surveyed. Of course, these findings vary regionally, with areas that are considered hot spots for the virus being more heavily impacted by agent absences.
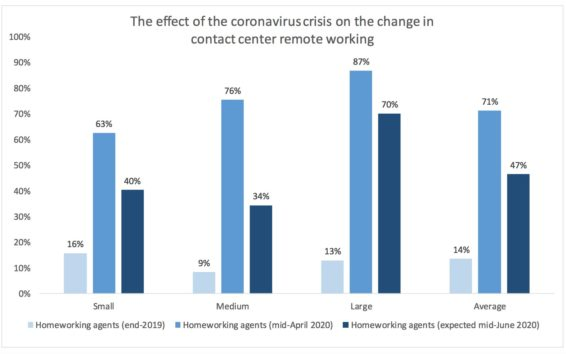
Prior to the outbreak at the end of 2019, only 14% of survey respondents’ agents had been homeworkers. By mid-April, that number had jumped to 71%, with larger companies most embracing this change.
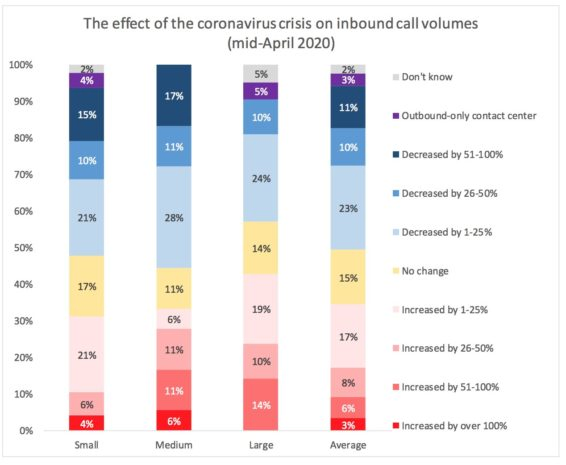
But to get a clearer picture, you need to look at results by vertical. While 34% of respondents show an increase in inbound call volume, 44% show a drop in the number of calls. However, these results are highly sensitive to the type of vertical. While businesses like banks, grocery stores and telecoms are experiencing an increase in calls, businesses like luxury goods retailers, claims departments for car insurers and public transportation providers likely have far lower than normal contact volumes.
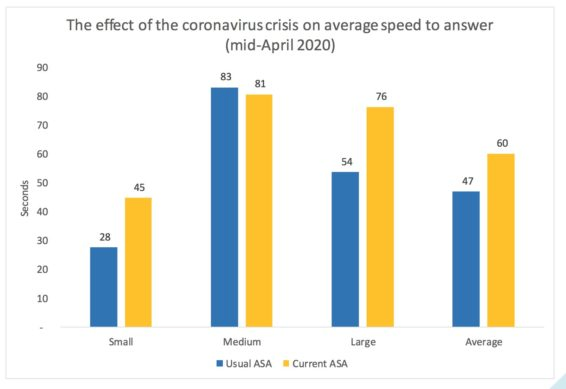
While mid-sized operations report a very slight drop in speed to answer, smaller and larger organizations are seeing a rise in average speed to answer, ranging from 40%-50%.
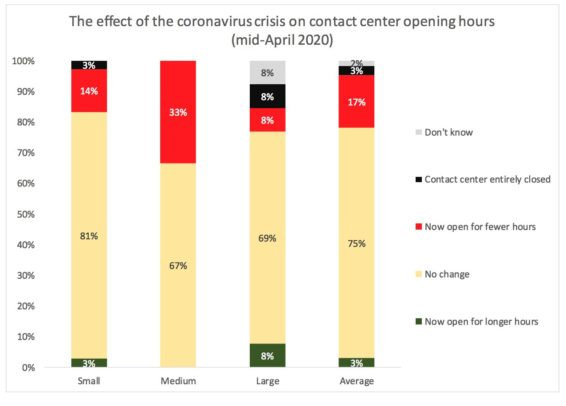
Three-quarters of respondents have not made any changes to their opening hours. One in six has cut hours and 3% have shut down operations entirely. Of the largest contact centres, 8% have increased their opening hours.
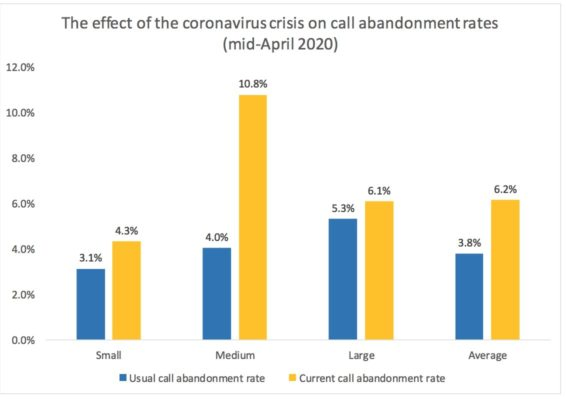
The cumulative effect of higher call volumes, longer speed to answer, longer opening hours and increased staff absence has been to increase call abandonment rates by about 60% industry-wide. This is an increase from 3.8% to 6.2%, according to respondent data. While all size businesses have seen a rise in call abandonment rates, this change is particularly noticeable in mid-sized businesses.
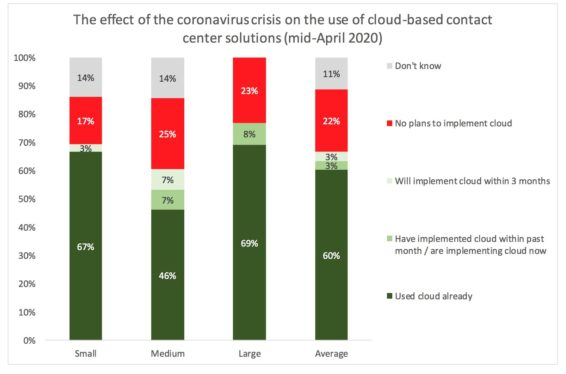
The increase in remote working is supported by an uptake in cloud-based contact centre solutions. And during the coronavirus pandemic, there has been a jump in the use of cloud, especially in mid-sized and large contact centre operations to support remote working and business continuity.
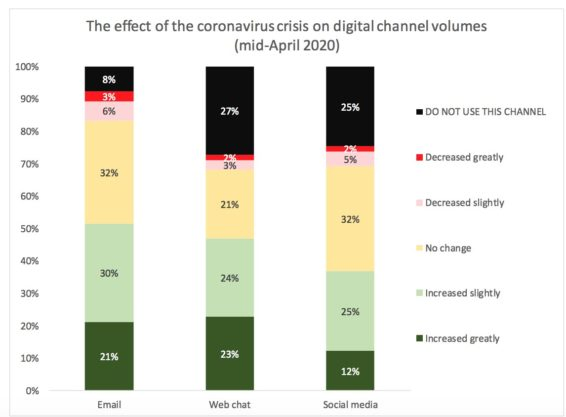
As customers try alternate ways of contacting businesses, there has been a growth in the use of all digital channels. Fifty-one percent of contact centres report increases in email use, 47% report increases in webchats and 37% report an increase in social media use.
For a clear picture of the current state of remote workforces within the contact centre, download the full report here. In addition to data on the impact of the coronavirus pandemic on contact centres, the report also offers information about how different contact centre solutions assist with remote working, how to approach cloud security for your virtual contact centre and how to manage a remote workforce.
You’ll also get access to data about customer behaviors and preferences for different types of interactions — from high emotion to high urgency to high complexity. In addition, the report covers the current role of digital channels, self-service and artificial intelligence, and looks at what the path forward for contact centres looks like once the crisis has passed.
To read the full report relating to the UK, download “The Inner Circle Guide to Contact Center Remote Working Solutions.” And learn more about Genesys Ready Response to avoid disruption in your contact centre.
Subscribe to our free newsletter and get the Genesys blog updates in your inbox.